
To successfully grow plant cuttings, select healthy stems, prepare them by cutting and removing excess leaves, and ensure optimal conditions like bright, indirect light and high humidity. Whether using soil or water for rooting, monitor moisture levels and transplant when roots are established for thriving new plants.
Are you eager to learn how to grow plant cuttings? This beginner-friendly guide will help you navigate the exciting world of plant propagation. Whether you’re looking to expand your garden or simply want to save money on new plants, understanding the basics of starting new life from cuttings is essential. In this article, we’ll discuss the different methods and tips to ensure you successfully grow healthy plants from cuttings.
Understanding Plant Cuttings

When it comes to understanding plant cuttings, it’s important to know what they are. Plant cuttings are small sections of a plant, typically including a stem or a leaf, that can be rooted to grow new plants. This method of propagation is popular among gardeners because it allows you to create new plants from existing ones. It’s an exciting way to expand your garden without needing to buy new plants.
Types of Cuttings
There are different types of cuttings, which include:
- Stem Cuttings: These are taken from the stem of a plant. They can be softwood, semi-hardwood, or hardwood, depending on the type of plant.
- Leaf Cuttings: These involve using just a leaf from the plant. Some plants can grow roots directly from the leaf.
- Root Cuttings: As the name suggests, these are segments taken from the roots of a plant.
Each type of cutting has its own method of propagation, but they all share the amazing ability to grow into new, independent plants.
Why Use Cuttings?
Using cuttings allows you to replicate plants you love. You can create new plants that maintain the same characteristics as the parent plant. This is especially useful for plants that are hard to find in stores or for preserving rare varieties.
By mastering the technique of taking and rooting cuttings, you’ll not only save money but also gain the satisfaction of growing plants from scratch. This method connects you with nature and enhances your gardening skills.
The Best Types of Plants for Cuttings

When you’re looking for the best types of plants for cuttings, there are several options that are known for their successful propagation. Many plants can be grown from cuttings, making it easier for gardeners to multiply their favorites. Here are some of the top plants that thrive from cuttings:
1. Pothos
Pothos is a popular houseplant that is incredibly easy to propagate. Just cut a stem with several leaves and place it in water or soil. It roots quickly and can grow in various lighting conditions.
2. Spider Plant
The spider plant produces offshoots called “pups” that can be easily cut off and planted. These plants are resilient and do well in many environments.
3. Coleus
Coleus comes in vibrant colors and thrives when propagated from cuttings. Just take a stem cutting below a leaf node and place it in water or soil.
4. Succulents
Many succulents, like jade and aloe, grow well from leaf or stem cuttings. Let the cutting dry for a day before planting it to prevent rot.
5. Geraniums
Geraniums are easy to grow from cuttings. Take a healthy stem cutting and place it in soil. They will root quickly and produce vibrant flowers.
6. Basil
Herbs like basil can also be propagated from cuttings. Place a stem in water until roots begin to form, then transfer it to soil. Fresh basil can enhance many dishes!
By selecting the right plants, you can expand your collection with minimal effort. Remember, the key is to take healthy cuttings and follow proper propagation techniques for the best results.
How to Prepare Cuttings for Rooting

Preparing cuttings for rooting is an essential step in the process of propagating new plants. Here’s how to effectively prepare your cuttings for rooting:
1. Choose Healthy Plant Material
Start with a healthy parent plant. Look for stems that are strong and free from disease. Damaged or diseased cuttings are less likely to root.
2. Make the Cut
Use clean, sharp scissors or a knife to take your cutting. Cut just below a leaf node, which is where new roots can grow. Aim for a cutting that is about 4 to 6 inches long.
3. Remove Extra Leaves
Trim off any leaves from the bottom half of the cutting. This helps prevent rot when planted in soil or water. Make sure at least one or two leaves remain at the top to allow for photosynthesis.
4. Use Rooting Hormone (Optional)
To enhance root development, consider using rooting hormone. Dip the cut end of your cutting into the hormone powder or gel before planting. This step can lead to faster and stronger root growth.
5. Prepare Your Medium
Decide whether you will root your cutting in soil or water. If using soil, ensure it is well-draining. For water, fill a clean glass or container, and place the cutting in it without the leaves touching the water.
6. Place in Suitable Environment
Put your prepared cuttings in a warm, bright location but out of direct sunlight. Ensure humidity is maintained, especially if using soil.
By following these steps, you can effectively prepare your cuttings for successful rooting, leading to new plants that will thrive.
Optimal Conditions for Growing Cuttings

Creating the optimal conditions for growing cuttings is crucial for their success. Here’s what you need to consider:
1. Light Requirements
Cuttings need bright, indirect sunlight to thrive. Too much direct light can scorch the leaves, while too little light can hinder root development. Place them in a spot where they receive filtered sunlight.
2. Temperature
Most cuttings do best in a temperature range of 65°F to 75°F (18°C to 24°C). Keeping them in a warm environment encourages faster root growth. Avoid placing cuttings near cold drafts or heat sources.
3. Humidity Levels
High humidity is important for cuttings because it prevents moisture loss. You can increase humidity by covering your cuttings with a plastic bag or placing them in a mini greenhouse. Mist them lightly to maintain moisture levels.
4. Airflow
Good airflow is essential to prevent mold and mildew from developing on your cuttings. While humidity is important, ensuring there is also enough ventilation will help keep them healthy.
5. Soil or Water Quality
If rooting in soil, use a light, well-draining potting mix. For water propagation, ensure that the water is clean and changed regularly to prevent algae growth. This set-up helps the cuttings absorb the nutrients they need.
6. Container Choice
Choose containers that allow for proper drainage. If using pots, make sure they have drainage holes. This helps prevent root rot and keeps the cuttings healthy.
By maintaining these conditions, you will create the perfect environment for your cuttings to root and grow into strong, healthy plants.
Watering Tips for Healthy Growth

Providing the right amount of water is crucial for the healthy growth of your cuttings. Here are some essential watering tips to keep in mind:
1. Watering Frequency
Check the soil or medium’s moisture before watering. Generally, cuttings should be watered when the top inch of soil feels dry. Avoid letting the soil completely dry out, as this can harm the cuttings.
2. Water Quality
Use clean, room-temperature water. If possible, let tap water sit for 24 hours to allow any chlorine to dissipate. This creates a healthier environment for root development.
3. Method of Watering
Water cuttings gently to avoid displacing them. Use a watering can with a spout or a spray bottle to distribute water evenly without over-soaking.
4. Avoid Overwatering
Overwatering can lead to root rot, which is a common problem. Always ensure that the containers have good drainage to prevent standing water. If cuttings sit in water for too long, they can develop unhealthy roots.
5. Adjust for Conditions
Adjust the watering frequency based on environmental conditions. In warmer temperatures or low humidity, cuttings may need more frequent watering. Conversely, in cooler or humid conditions, they may need less.
6. Observe Your Cuttings
Keep an eye on your cuttings for signs of stress. Yellowing leaves can indicate overwatering, while wilting leaves may suggest underwatering. By observing these signs, you can adjust your watering routine accordingly.
Following these watering tips will help ensure that your cuttings thrive and develop into healthy plants.
Using Soil vs. Water for Rooting

When propagating plant cuttings, you often have to choose between using soil or water for rooting. Each method has its own benefits and challenges.
Using Soil for Rooting
Rooting cuttings in soil is a popular method among gardeners. Here are some key points:
- Advantages: Soil provides necessary nutrients and support for new roots, mimicking natural conditions.
- Best for: Most plants prefer soil for rooting, especially those that thrive in garden beds or pots.
- Technique: Use a well-draining potting mix, and ensure pots have drainage holes to prevent root rot.
- Moisture Level: Keep the soil consistently moist but not soggy, checking regularly.
Using Water for Rooting
Rooting cuttings in water is a simple and effective method. Consider these aspects:
- Advantages: You can easily see the root development, which helps in assessing progress.
- Best for: Some plants, like pothos and coleus, root well in water.
- Technique: Use a clean jar or glass, placing the cuttings in water while ensuring no leaves touch the water.
- Water Care: Change the water every few days to prevent algae and keep it fresh.
Both methods can successfully produce new plants, so you can choose the one that works best for you. Experimenting with both techniques allows you to find your preferred approach based on specific plants and your gardening style.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When propagating plant cuttings, avoiding common mistakes can make a big difference in success rates. Here are some of the most frequent errors to watch out for:
1. Using Dull Tools
Always use clean and sharp scissors or a knife when taking cuttings. Dull tools can crush stems, making it harder for them to root. Clean cuts promote healthier growth.
2. Ignoring Parent Plant Health
Taking cuttings from a sick or stressed plant is a mistake. Always choose cuttings from healthy plants, as this increases the chances of successful rooting.
3. Overwatering or Underwatering
Finding the right balance in watering is essential. Overwatering can lead to root rot, while underwatering can cause cuttings to wilt. Check moisture levels regularly to avoid these issues.
4. Not Providing Enough Light
Cuttings need bright, indirect light. Placing them in too much direct sunlight can scorch their leaves. Make sure to find a spot that offers filtered light.
5. Neglecting Humidity
Many cuttings benefit from high humidity to prevent moisture loss. Use plastic bags or humidity domes to retain moisture, especially in dry environments.
6. Forcing Transplanting Too Soon
It’s tempting to move cuttings to larger pots once they show roots, but wait until they are well-established. Transplanting too soon can shock the young plants.
7. Failing to Label Cuttings
When propagating multiple types of cuttings, failure to label them can lead to confusion. Keep track of the plant species to know which care is needed.
Avoiding these common mistakes can significantly improve the success rate of your plant cuttings. By being attentive and careful, you can enjoy a thriving garden in no time.
When to Transplant Your Cuttings
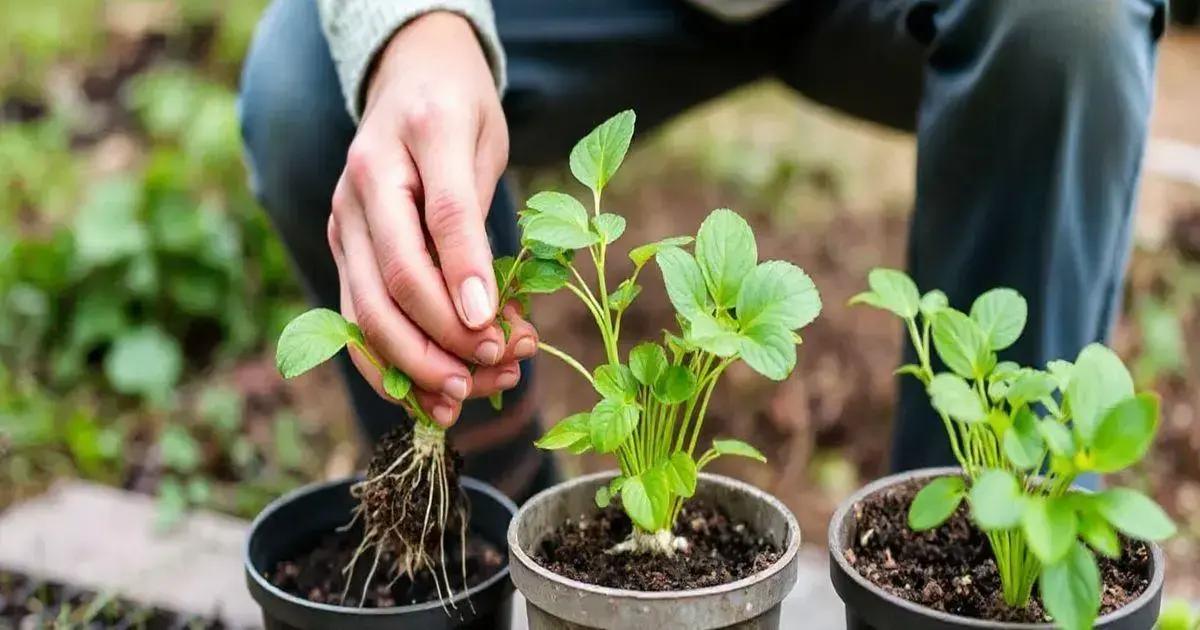

Knowing when to transplant your cuttings is vital for their health and growth. Here are the signs that indicate your cuttings are ready for transplanting:
1. Established Roots
A cutting is ready to be transplanted when it has developed a strong and healthy root system. You can check this by gently pulling it out of the soil or container and examining the roots. They should be at least a few inches long and white or light tan in color.
2. Growth of New Leaves
Look for new leaf growth on your cutting. If you see fresh leaves forming, it’s a good indication that the plant is thriving and ready to move to a larger pot.
3. Crowded Container
If the cutting is outgrowing its current container, with roots filling the pot or water vase, it’s time to transplant it. A crowded environment can prevent growth and lead to stress.
4. Healthy Appearance
Transplant when the cutting appears healthy. Avoid transplanting if the cutting looks stressed, wilting, or yellowing, as this can affect its ability to adapt to new soil or conditions.
5. Seasonal Considerations
The best time to transplant is in spring or early summer when plants are actively growing. This allows the cutting to quickly establish itself in its new environment.
Transplanting your cuttings at the right time encourages robust growth and ensures that they have the best chance of thriving in their new home. By monitoring these signs, you can give your cuttings the best start possible.
In Conclusion, Success in Growing Plant Cuttings
Growing plant cuttings can be a rewarding and enjoyable process when done correctly. By understanding the fundamentals, such as selecting the right types of plants, preparing cuttings effectively, providing optimal conditions, and being aware of common mistakes, you set yourself up for success.
Utilizing both soil and water for rooting gives you flexibility based on your preferences and the plants you are working with. Proper watering techniques and knowing the right time to transplant will further ensure that your cuttings thrive.
With these guidelines, you can cultivate a healthy garden filled with new plants, showcasing your gardening skills and dedication. Happy planting!
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Growing Plant Cuttings
What are plant cuttings?
Plant cuttings are pieces of a plant, such as stems or leaves, that can be rooted to grow new plants.
How do I prepare cuttings for rooting?
To prepare cuttings, select healthy stems, cut them below a leaf node, remove extra leaves, and optionally use rooting hormone.
What are the best conditions for growing cuttings?
Cuttings thrive in bright, indirect light, with temperatures between 65°F to 75°F, high humidity, and proper airflow.
Should I use soil or water to root my cuttings?
You can root cuttings in either soil or water. Soil provides nutrients while water allows you to easily monitor root development.
When should I transplant my cuttings?
Transplant your cuttings when they have established roots, show new leaf growth, or appear healthy. Spring is an ideal time.
What are common mistakes to avoid when propagating cuttings?
Common mistakes include using dull tools, overwatering or underwatering, inadequate light, and transplanting too soon.
About the Author




0 Comments