
A vertical garden is an innovative gardening method that allows plants to grow in a vertical space, maximizing limited areas for greenery. By selecting the right materials, plants, and irrigation systems, you can create a thriving and visually stunning vertical garden in your home.
How to build a vertical garden is a great way to maximize your available space while enhancing the beauty of your home. Whether you’re in a small apartment or have limited outdoor space, vertical gardens offer a solution. This article covers how to create a lush, green display that’s not only appealing but also functional. From selecting the right plants to understanding the necessary tools, we’ll guide you through each step of the process.
Understanding Vertical Gardens
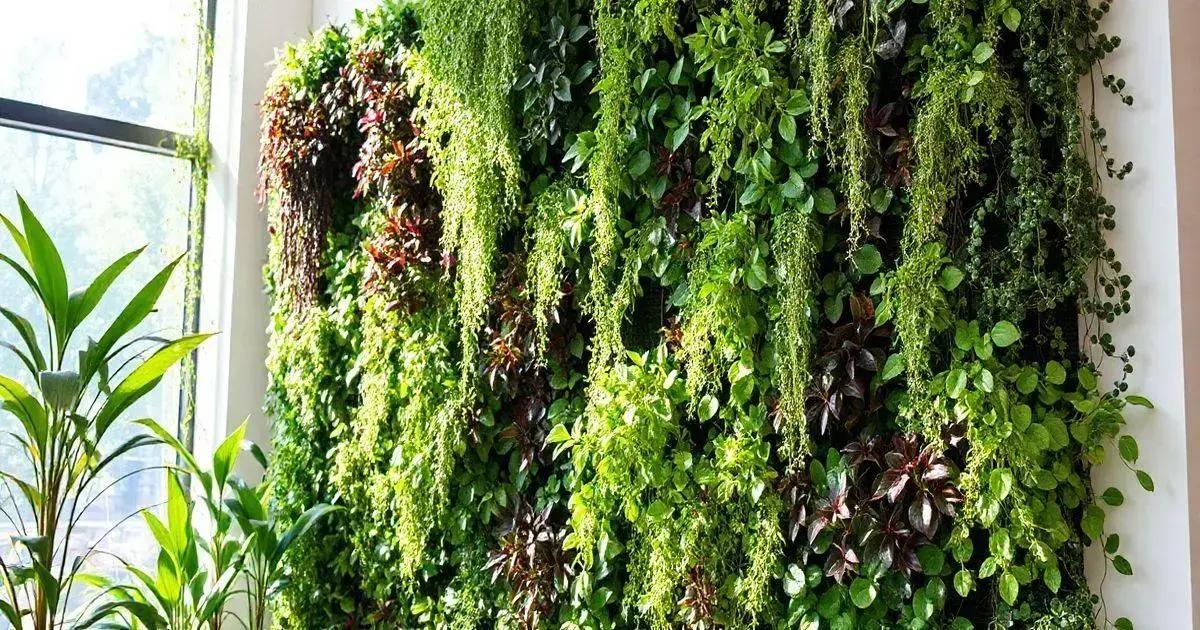

Understanding Vertical Gardens is essential for anyone looking to bring greenery into their living space. These innovative gardens take advantage of vertical space, allowing you to grow plants upwards rather than outwards. This is especially useful in urban settings where ground space is limited.
What is a Vertical Garden?
A vertical garden, also known as a living wall or green wall, is a garden that is vertically suspended or mounted. It can be created using various materials, including panels, pots, and trellises, which support the plants as they grow. It typically consists of layers of soil, plants, and a support structure.
Benefits of Vertical Gardens
Vertical gardens offer numerous advantages. They can improve air quality, reduce noise pollution, and increase biodiversity. Additionally, they provide insulation for buildings, helping to reduce energy costs. Plus, they add aesthetic value to both indoor and outdoor spaces.
Space Efficiency
One of the main reasons for choosing a vertical garden is to maximize the use of limited space. You can transform small patios, balconies, or even indoor walls into thriving plant displays. This makes vertical gardens perfect for urban dwellers.
Types of Vertical Gardens
There are a few different types of vertical gardens, including modular systems, hydroponic walls, and traditional gardens supported by trellises. Modular systems make it easier to maintain and replace plants, while hydroponic setups are more suited for those who want to grow edibles without soil.
Design Flexibility
Vertical gardens can be designed in various styles, from structured geometric shapes to flowing, natural arrangements. This flexibility allows you to personalize your garden to suit your aesthetic and the available space. You can choose to display a single type of plant or a diverse mix for added visual interest.
Conclusion
Understanding the concept of vertical gardens can inspire you to create your own green oasis. Once you grasp the basics, you can explore how to effectively design and cultivate a vertical garden that meets your space and lifestyle needs.
Choosing the Right Location
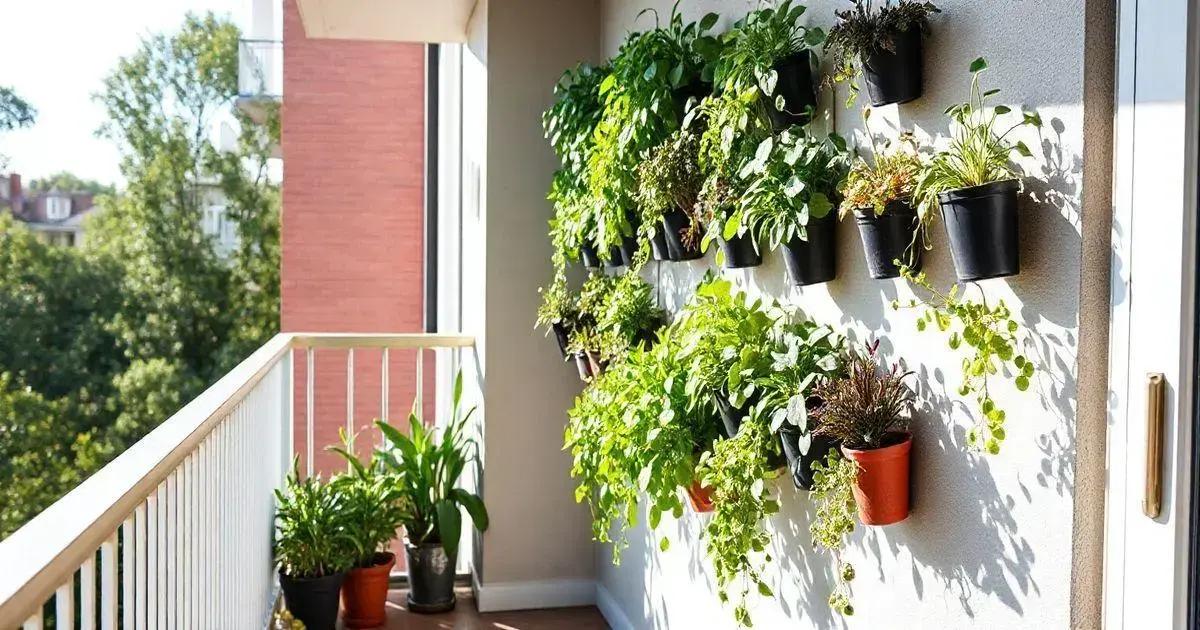

Choosing the right location for your vertical garden is crucial to its success. Different plants have varying light and space needs, so assessing your environment is the first step.
Assess Light Conditions
Most plants require sunlight to thrive. When selecting a spot for your vertical garden, observe how much sunlight the area gets throughout the day. Full sun areas receive 6-8 hours of direct sunlight, while partial shade areas get 3-6 hours. Shaded areas receive less than 3 hours. Choose plants that match the light level of your chosen location.
Consider Accessibility
Your vertical garden should be easily accessible for maintenance. Consider how often you will need to water and prune the plants. The location should allow you to reach the garden comfortably without too much effort. Hanging gardens should be stable and easy to manage.
Check Wall Weight Limits
If you plan to mount your vertical garden on a wall, make sure the structure can support the weight of the plants, soil, and water. For larger gardens, consult a professional to ensure your wall can handle the load. Wood, brick, or concrete walls may have different capabilities.
Evaluate Microclimates
Microclimates are small areas that can have different climatic conditions than the surrounding area. Observe your chosen spot for any unique characteristics, such as shelter from winds or heat. Areas near walls may retain heat, while shaded areas may stay cooler. Understanding these factors helps in selecting appropriate plants.
Plan for Drainage
Good drainage is vital to prevent waterlogging and root rot in your vertical garden. Make sure your chosen location can efficiently drain excess water. If you’re building an indoor vertical garden, ensure you have a way to manage water runoff.
Safety Considerations
Lastly, consider safety. Avoid locations that may have falling debris or hazards nearby. Ensure that the vertical garden does not block any doors, windows, or emergency exits. Keep in mind how weather will affect the placement of your garden.
Selecting Plants for Your Vertical Garden
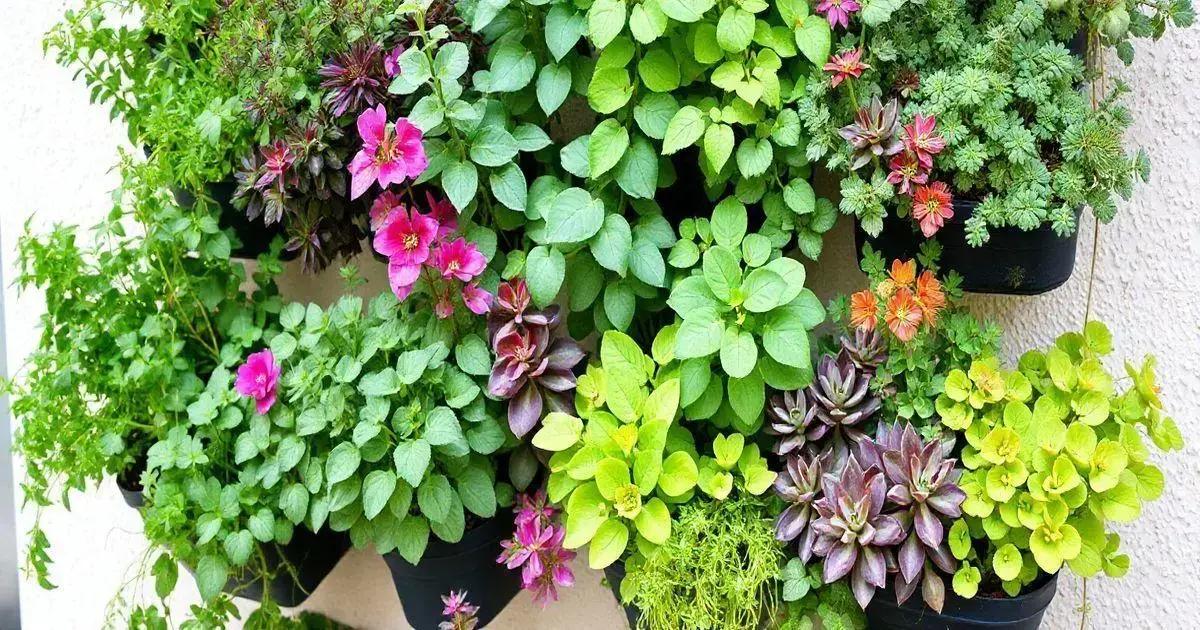

Selecting the right plants for your vertical garden is essential for success. Different plants have unique needs concerning sunlight, water, and space. Here are some tips to help you choose effectively.
Understanding Plant Types
When selecting plants, it’s crucial to know that there are generally two types: decorative and edible. Decorative plants, such as ferns and succulents, are often chosen for aesthetics, while edible plants, including herbs and vegetables, provide functional benefits. Consider which type fits your goals.
Light Requirements
Evaluate the light conditions in your garden’s chosen location. Some plants thrive in full sunlight, while others prefer shade or indirect light. For sunny spots, choose plants like petunias or cherry tomatoes. For shadier areas, consider ferns or ivy.
Size and Growth Habit
Consider the size of the plants at maturity. Tall plants should be placed at the back of the structure to avoid overshadowing shorter plants. Compact varieties work best in small spaces. Ensure plants with different growth habits can coexist without overcrowding.
Watering Needs
Different plants have varying water requirements. Group plants with similar watering needs together to simplify your irrigation process. For example, lavender and succulents need less water, while ferns require more moisture.
Seasonal Considerations
Depending on the climate, consider planting combinations that can thrive in all seasons. For instance, choose hardy plants that can survive colder months, and incorporate annual flowers for seasonal color changes.
Local Climate Adaptability
Select plants that are well-suited for your local climate. Native plants tend to adapt better, requiring less maintenance and water. Consult local gardening guides or nurseries for recommendations on suitable species.
Creating Visual Interest
Diversifying your plant selection adds visual appeal. Combine a mix of colors, textures, and shapes for stunning displays. Use trailing plants like golden pothos alongside upright varieties for a layered effect.
Materials for Vertical Structure
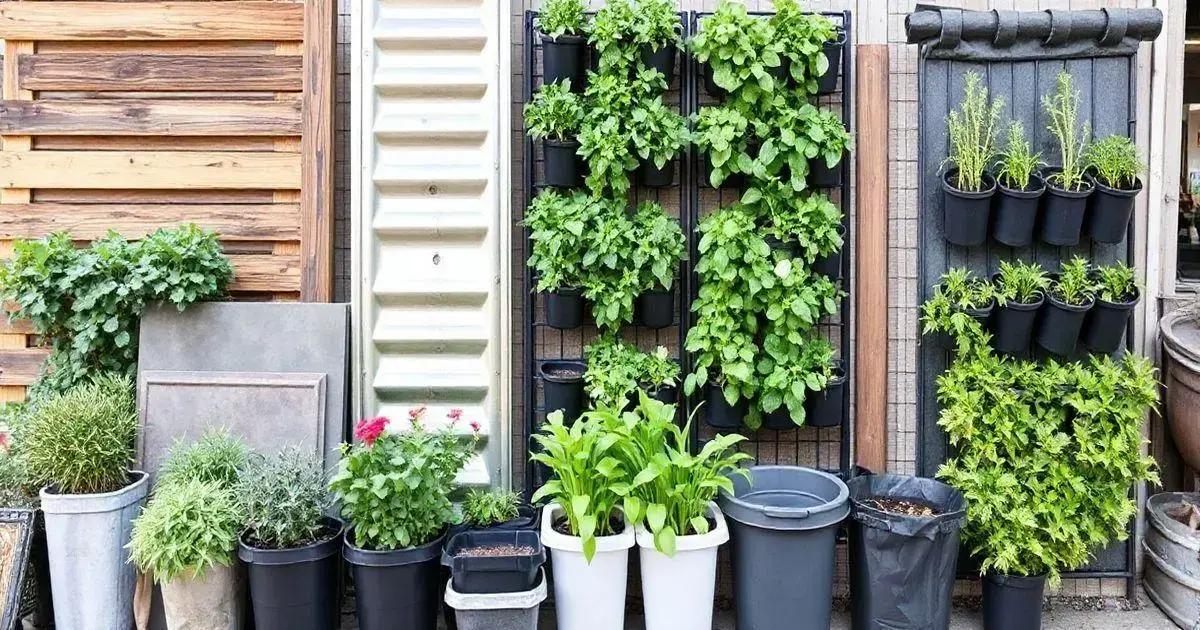

Choosing the right materials for your vertical garden structure is vital for its stability and success. Several options are available, and the right choice depends on where you’ll place your garden and the types of plants you want.
Wood
Wood is a popular choice for vertical gardening structures because it is durable and visually appealing. Cedar and redwood are great options due to their natural resistance to rot. Make sure to treat the wood to enhance its durability, especially for outdoor gardens.
Metal
Metal frames provide strength and stability to vertical gardens. Galvanized steel or aluminum can withstand outdoor conditions. These materials can be designed into various shapes and sizes. Ensure proper drainage if you’re using metal to prevent rusting.
Plastic Containers
Plastic containers are lightweight and affordable options. They are UV-resistant and come in various colors and designs. When using plastic, ensure that it has sufficient drainage holes for plant health. Stackable or vertical planting containers can also optimize space.
Wire Mesh
Wire mesh supports climbing plants beautifully and can be used in conjunction with other materials. It allows plants to cling and grow vertically. Your wire mesh should be sturdy enough to hold the weight of the plants as they grow.
Fabric Planters
Fabric planters are an excellent lightweight option, making them easy to hang on walls. They allow for good drainage and air circulation, which benefits root health. They also come in various styles that can match your decor.
Growing Medium
A good growing medium is vital for plant health. Use a mix of potting soil, compost, and perlite to ensure proper nutrients and drainage. Ensure the medium is lightweight enough to prevent stress on the structure.
Hanging Hardware
Consider using strong hanging hardware to support your vertical garden. Use brackets, hooks, and anchors designed for the weight of your garden. If you’re mounting on a wall, find studs or use wall anchors for added support.
How to Assemble Your Vertical Garden
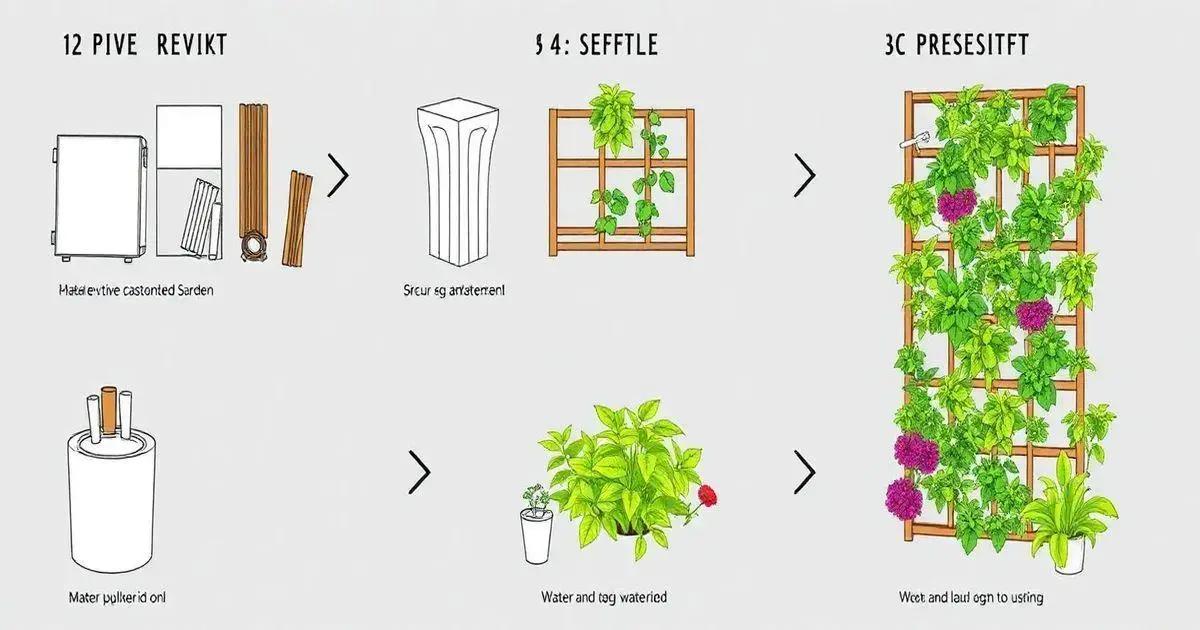
Assembling your vertical garden may seem daunting, but breaking it down into steps makes it manageable. Follow these steps to create a thriving garden.
Step 1: Gather Your Materials
Ensure you have all the necessary materials, including your chosen structure (wood, metal, etc.), plant containers, suitable growing medium, plants, and hanging hardware. Having everything on hand will streamline the assembly process.
Step 2: Prepare the Structure
Before you begin, prepare your vertical garden structure. If using wood, ensure it is treated for outdoor use. For metal, double-check that it is clean and rust-free. If it’s a wall-mounted garden, locate the wall studs and mark their positions for secure installation.
Step 3: Attach the Structure Securely
Mount the vertical garden structure on the chosen wall or fence. Use appropriate hardware, such as brackets or heavy-duty screws, to secure it firmly. It should be sturdy enough to hold the weight of the plants and soil.
Step 4: Arrange the Containers
If using individual containers, arrange them on the structure in a way that suits your design. Consider plant height and growth habits—tall plants should be at the back, while trailing plants can hang in the front for visual interest. Mark where the containers will go to maintain uniform spacing.
Step 5: Fill with Growing Medium
Fill each container with your chosen growing medium. A good mix may include potting soil, compost, and perlite for drainage. Leave some space at the top of each container to prevent spillage when watering.
Step 6: Plant Your Selections
Begin placing your plants in the containers. Be gentle with the roots and ensure they are adequately spaced to allow for growth. If they’re small, group them closer; for larger plants, ensure enough room to thrive.
Step 7: Water the Plants
Once all the plants are placed, give them a good watering to settle the soil. Make sure the water drains well, especially if you’ve used a structure that doesn’t have drainage holes.
Step 8: Install Irrigation Solutions
If your vertical garden is large, consider installing an irrigation system for consistent watering. Drip irrigation can be an efficient solution. Otherwise, ensure you check and water the garden regularly based on the plant needs.
Irrigation Solutions for Vertical Gardens
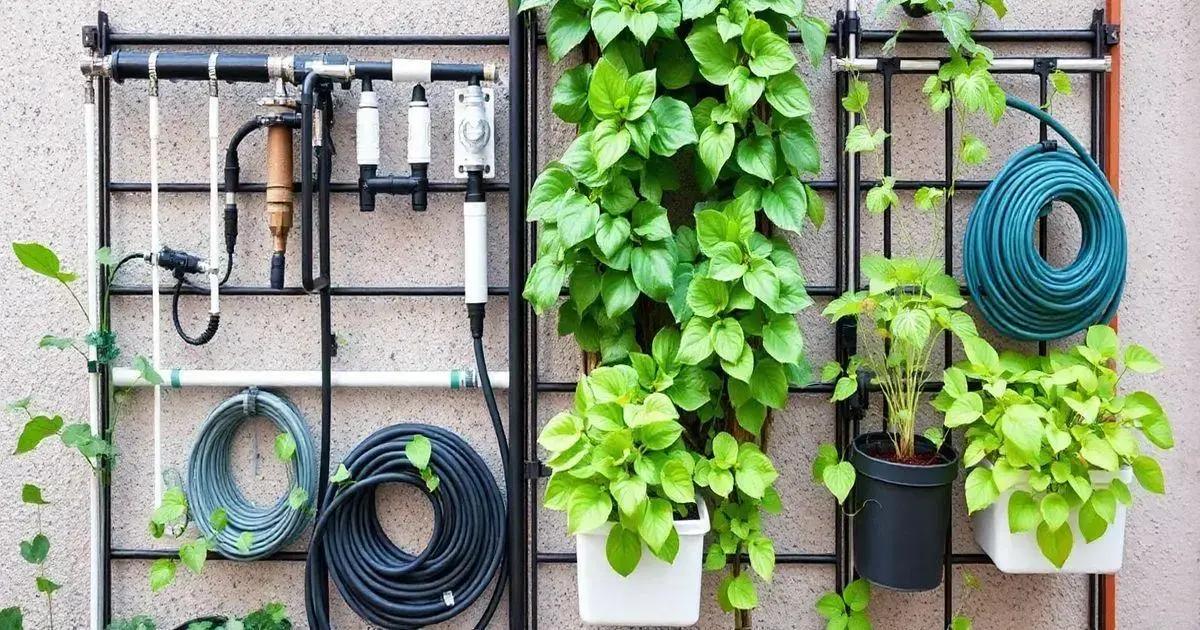

Choosing the right irrigation solution for your vertical garden is crucial for the health of your plants. Here are some effective methods to ensure your plants receive adequate water.
Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation is one of the most efficient ways to water vertical gardens. This system delivers water directly to the roots, minimizing waste. Installing a drip system can be done with a few tubes and emitters placed at each plant. This setup allows consistent and controlled watering.
Soaker Hoses
Soaker hoses are also a good option. They gradually release water along their length, soaking the soil deeply. Lay the soaker hose in a zigzag pattern throughout your vertical garden. They are easy to use and can be connected to a standard faucet.
Hand-Watering
If your vertical garden is small, hand-watering can be effective. Use a watering can or a hose with a spray nozzle. Make sure to water at the base of each plant to avoid wetting the leaves. Check soil moisture regularly to adjust your watering schedule.
Self-Watering Containers
Self-watering containers are ideal for vertical gardening. They have a reservoir at the bottom that supplies moisture to the plants as needed. This reduces the frequency of watering and helps maintain consistent soil moisture.
Rainwater Collection
Consider installing a rainwater collection system. This eco-friendly method uses rainwater to irrigate your vertical garden. Use barrels or tanks to collect rainwater and connect it to your irrigation system. This is a sustainable solution that conserves resources.
Smart Irrigation Systems
For tech-savvy gardeners, smart irrigation systems can automate your watering. These systems use sensors to monitor soil moisture and weather conditions, providing water only when needed. They can connect to mobile apps for full control.
Regular Monitoring
No matter which irrigation method you choose, regular monitoring is essential. Observe your plants for signs of under-watering or over-watering, such as yellowing leaves or wilting. Adjust your irrigation accordingly to ensure a healthy vertical garden.
Maintaining Your Vertical Garden

Maintaining your vertical garden is essential for keeping it healthy and vibrant. Regular care will help your plants thrive. Here are some key maintenance tips to follow.
Watering Schedule
Establish a consistent watering schedule based on your plant requirements. Check the soil moisture regularly. Most vertical gardens benefit from watering every 2-3 days but adjust based on weather and plant type. Deep watering is better than shallow watering to encourage strong root growth.
Fertilizing
Adding fertilizer helps provide essential nutrients that plants need to grow. Use a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer every 4-6 weeks, especially during the growing season. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer package to avoid over-fertilizing, which can harm your plants.
Pest Control
Monitor your vertical garden for signs of pests, such as aphids and spider mites. Hand-pick pests when possible and use insecticidal soap if infestations occur. Preventive measures like introducing beneficial insects, such as ladybugs, can also help control pest populations.
Pruning and Trimming
Regular pruning promotes healthy growth and prevents overcrowding. Remove dead or yellowing leaves to improve air circulation. Trim back any plants that are outgrowing their space to maintain a neat appearance and allow light to reach all plants.
Checking for Diseases
Keep an eye on your plants for any signs of disease, such as wilting or discolored leaves. Early detection is key. Remove affected leaves immediately to prevent the spread of the disease and treat with appropriate fungicides if necessary.
Seasonal Changes
Adjust your care routine based on the seasons. In winter, many plants slow their growth, so reduce watering and fertilizing. Protect tender plants from frost by moving them indoors or covering them during harsh weather conditions.
Cleaning and Maintenance of Structure
Periodically clean the structure of your vertical garden. Remove any debris that may accumulate and check for wear on containers and supports. This ensures the structure remains secure and visually appealing.
Common Issues and Solutions

Even with the best planning, common issues can arise in vertical gardens. Understanding these problems and knowing how to address them is key to a successful garden.
Problem: Wilting or Yellowing Leaves
Wilting or yellowing leaves often indicate either overwatering or underwatering. Check the soil moisture; if it feels soggy, reduce watering frequency. Conversely, if the soil is dry, increase the amount of water you give your plants. Always ensure your containers have proper drainage to avoid root rot.
Problem: Pest Infestations
Pests like aphids, spider mites, and mealybugs can harm your plants. Regularly inspect your vertical garden for any signs of pests. If found, treat smaller infestations with natural remedies like insecticidal soap or neem oil. For larger infestations, consider using stronger pesticides while ensuring safe practices.
Problem: Poor Growth or Flowering
If your plants are not growing well or blooming, they may be lacking essential nutrients. Fertilize your garden every 4-6 weeks with a balanced fertilizer to provide necessary nutrients. Also, reconsider the plant selection based on sunlight and growing conditions.
Problem: Root Bound Plants
Plants can become root-bound in their containers, which stunts their growth. If you notice roots growing out of the drainage holes, consider transplanting them into larger containers or trimming the roots to promote new growth.
Problem: Disease Spread
Disease can spread quickly in vertical gardens, especially during high humidity. Monitor your plants for signs of disease, such as wilting, discoloration, or mold. If you suspect disease, remove affected plants immediately and sanitize surrounding areas to prevent further spread.
Problem: Structural Issues
Over time, the structure supporting your vertical garden may weaken. Regularly check for any signs of wear or damage. Ensure all attachments are secure and consider reinforcing areas showing signs of stress. Replace any compromised materials to safeguard your garden.
Problem: Inconsistent Watering
Inconsistent watering can lead to stressed plants and uneven growth. Set up an irrigation timer to ensure consistent watering during the growing season. Additionally, inspect your watering systems regularly for clogs or leaks.
In Conclusion: Your Pathway to a Thriving Vertical Garden
Building and maintaining a vertical garden can transform your living space into a vibrant green oasis. By understanding the intricacies of choosing the right location, selecting suitable plants, and assembling the proper materials, you lay a solid foundation for your garden.
Regular maintenance, including effective irrigation solutions, is key to keeping your plants healthy and thriving. Addressing common issues promptly helps prevent larger problems down the road. Whether combating pests or ensuring consistent watering, being proactive will yield a lush vertical garden.
Vertical gardens not only enhance aesthetics but also offer sustainable benefits, making them a great addition to any home. With dedication and care, you can enjoy the beauty and freshness of a vertical garden for years to come.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About Vertical Gardening
What is a vertical garden?
A vertical garden is a gardening system that allows plants to grow upwards instead of outwards, often using wall-mounted structures or panels.
What types of plants can I use in a vertical garden?
You can use both decorative and edible plants, such as herbs, succulents, ferns, and flowering plants that suit your climate and light conditions.
How often should I water my vertical garden?
Most vertical gardens benefit from watering every 2-3 days, but you should check the soil moisture and adjust based on the plants’ needs.
What common problems might I encounter with my vertical garden?
Common issues include wilting or yellowing leaves, pest infestations, poor growth, and diseases. Regular monitoring can help detect problems early.
How can I efficiently irrigate my vertical garden?
Irrigation methods include drip irrigation, soaker hoses, hand-watering, and self-watering systems. Choose based on your garden size and plants’ needs.
What materials are best for building a vertical garden?
Durable materials like treated wood, metal, plastic containers, and wire mesh are excellent choices for creating a stable vertical garden structure.
About the Author


0 Comments